Breakthrough in Green Technology: Researchers Develop Hydrate-Based Method for SF6 Sequestration
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential 23,900 times that of carbon dioxide, has seen its emissions steadily rise over time. In response to this environmental challenge, researchers have proposed an innovative solution: hydrate-based technology for SF6 sequestration.
The research team led by Prof. Lei Jiang from the Department of Experimental Study under Deep-sea Extreme Conditions (IDSSE), in collaboration with the National University of Singapore and the Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, recently conducted a study on the thermodynamic and kinetic properties of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) hydrates.
The study, conducted by a leading research team, unveiled the following key findings:
1.Thermodynamic Stability: Experiments confirmed that SF6 hydrates remain stable under low-pressure conditions, offering a viable approach to sequestration (Figure 1a).
2.Molecular Insights: Advanced molecular simulations revealed that SF6 molecules exclusively occupy large cages within the hydrate structure. Raman spectroscopy further validated this, identifying a distinct Raman shift from ~770 cm⁻¹ to ~777 cm⁻¹ as a signature of SF6 encapsulation (Figure 1b, 1c).
3.Kinetic Advancements: Kinetic studies demonstrated that low-pressure conditions in seawater systems significantly enhance the formation of SF6 hydrates, paving the way for efficient capture and storage (Figure 1d).
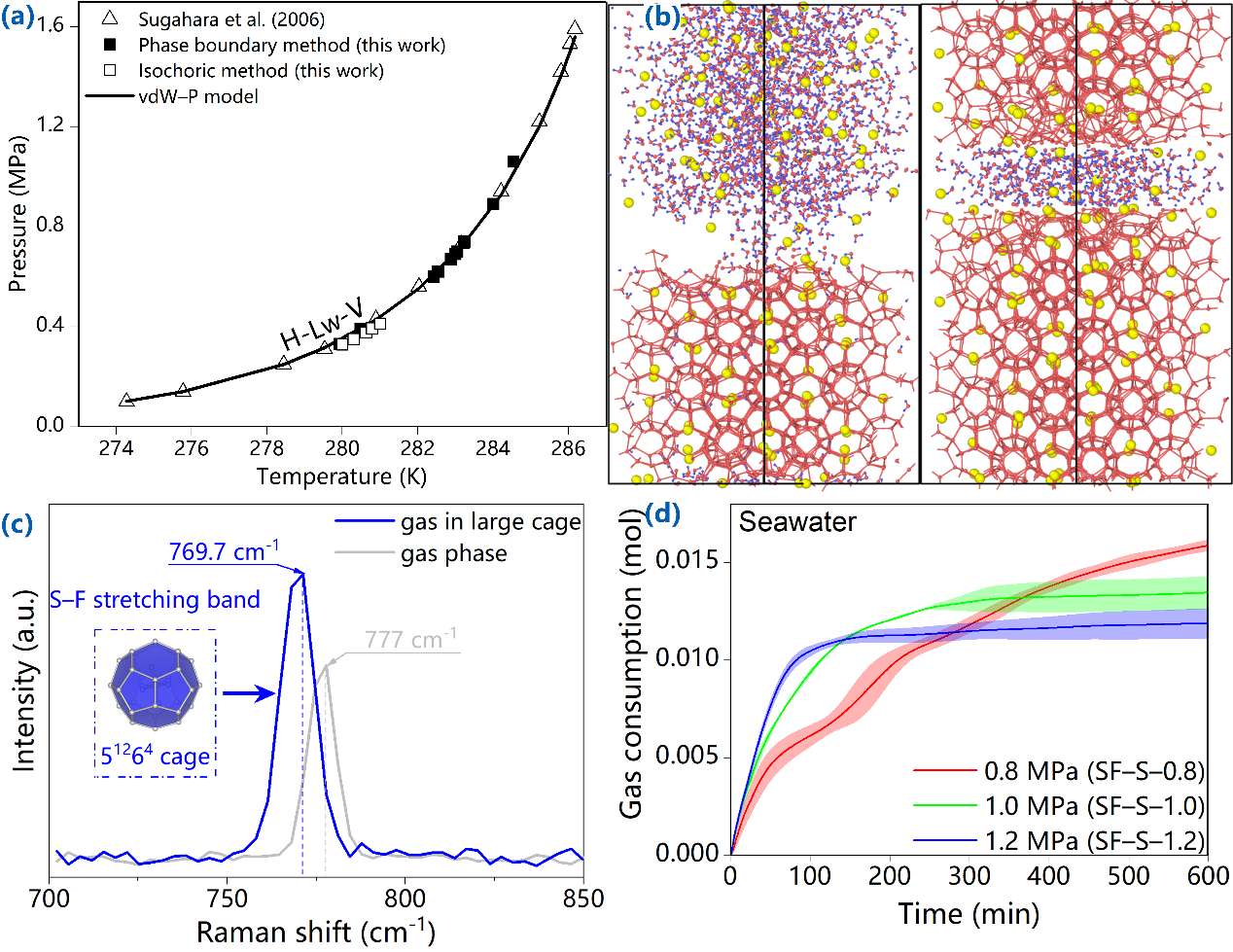
Figure 1. (a) Measurements and predictions along the three-phase coexisting curve for the SF6 hydrate system, (b) Snapshots captured at different moments for the SF6 hydrate system, (c) S–F stretching bands of SF6 in large cages and gas phase, (d)the gas consumption for the SF6–seawater system
These findings mark a significant step forward in mitigating SF6 emissions and highlight the potential of hydrate-based technology as a promising solution for environmental sustainability.
The research paper titled “Hydrate–based SF6 capture and sequestration: Insights from thermodynamics, kinetics, in–situ Raman spectroscopy, and molecular dynamic simulation” has been published in the international academic journal “Chemical Engineering Journal”. Dr. Jiyue Sun, a postdoctoral researcher, is the first author of the paper, and Prof. Lei Jiang serves as the co-corresponding author.